| Mike's Pages |
Links |
Oxidization states of metal atoms in linear bimetallic multi-sandwich molecules Vn(FeCp2)(n+1) and magnetic moment enhancement mechanism of its 1D wire
Lei Shen, Hongmei Jin, Valeri Ligatchev, Shuo-Wang Yang, Michael B. Sullivan and Yuanping Feng
Institute of High Performance Computing, 1 Fusionopolis Way, #16-16 Connexis, Singapore 138632, Singapore. Department of Physics, National University of Singapore, Singapore 117542, Singapore
Received 24th December 2009 , Accepted 24th February 2010, First published on the web 15th March 2010
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 4555-4559.
ABSTRACT:
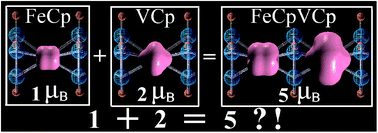
Using density functional theory calculations, we demonstrate that one-dimensional bimetallic molecular ferromagnets (FeCpMCp)∞ (M = Sc, Ti, V, Cr and Mn, Cp = cyclopentadienyl) exhibit significant enhancement in local and global atomic magnetic moments as well as relatively large spin-polarization energy as compared to their monometallic counterparts. These yield an unusual charge configuration for one of the wires: (Fe0Cp-1 V+2Cp-1)∞. Hückel's rule and double-exchange interaction model are used to illustrate the details of local charge transfer and long-range ferromagnetic order. We then propose a growth mechanism for Vn (FeCp2)(n+1) (n = 1-4) clusters, which is supported unambiguously with time-of-flight mass spectroscopy data.
DOI: 10.1039/b927272k