| Mike's Pages |
Links |
A Density Functional Theory study of CO oxidation on Pd-Ni alloy with sandwich structure
F.C.H. Lim, J. Zhang, H.M. Jin, M.B. Sullivan, P. Wu
Institute of High Performance Computing, Agency for Science, Technology and Research, Singapore, 1 Fusionopolis Way, #16-16 Connexis Singapore 138632 and Singapore University of Technology and Design, 20 Dover Drive Singapore 138682
Accepted: 8 November 2012; published online 21 November 2012
Appl. Cat. A 2013, 451, 79-85.
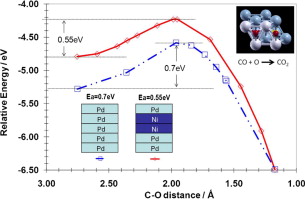
ABSTRACT:
Density functional theory calculations are performed to study CO oxidations on pure Pd(111) surface as well as on its Ni alloy nanostructures. Our calculations demonstrate a dependency of catalytic properties to the Ni occupancy site in the alloys. Furthermore, our results also show that optimal compressive strain (around 5%) of the alloy maybe beneficial to lower the reaction barrier and a compressive strain beyond 7% induces a distortion on the surface that eliminate the adsorption site for the reacting species. Based on our results, we propose that the Pd-Ni alloy with sandwich structure could be a potential candidate identified for lowering the cost of Pd alloys in the catalysis the CO oxidation reaction. This new structure illustrates a potential lowering in the CO oxidation barrier on a Pd-Ni-Pd surface sandwich slab. Furthermore, our results also indicate that the partial replacement of cheaper Ni into the Pd catalyst should not adversely affect the catalytic property.